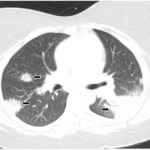
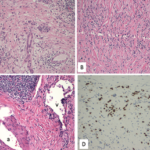
Eighteen months later, the patient developed cough and dyspnea on exertion and was diagnosed with pneumonia at another facility. He was treated with antibiotics and adalimumab was discontinued. His shortness of breath persisted, and a CT of the chest noted lymphadenopathy and bilateral pleural effusions. He was subsequently referred to thoracic medicine clinic at our institution. PFTs revealed significantly decreased mid flow and forced expiratory flow (FEF 25–75%), suggestive of small airway limitation. Serum calcium was 9.0 (8.3–10.5 mg/dl) and ACE level 38 (9–67 U/L). Bronchoscopy with lymph node FNA was performed, with histological findings showing a mixed population of lymphocytes with granulomatous inflammation, negative for malignant cells (see Figure 3). Flow cytometry revealed a reactive population of B and T lymphocytes. The diagnosis was thought to be sarcoidosis and, because this disease began while on a TNF inhibitor, no further drugs of that class were initiated.
The patient remained on varying doses of prednisone and naproxen due to lack of follow-up and noncompliance. He gained significant weight while on prednisone. Eventually, after his compliance improved, methotrexate was restarted and his joint pain improved, but his skin lesions persisted despite additional treatment with topical corticosteroids. There has been no change in the appearance of his hilar adenopathy and there are no new parenchymal lung lesions.
Although the complete pathophysiology of sarcoidosis is not well understood, it is known that TNF-α plays a major role in sarcoidosis development, and TNF-α inhibitors have been used for the treatment of refractory sarcoidosis. In contrast, a few case reports have described a paradoxical effect, with TNF-α inhibitor therapy leading to the development of granulomatous disease or sarcoidosis.
Discussion
In this report, we described two new cases of pulmonary sarcoidosis that occurred during treatment with TNF-α inhibitor therapy in patients with psoriatic arthritis.
Granuloma formation is central in the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis, possibly as a result of an exaggerated immune response to an unknown environmental antigen.3 Granuloma formation starts with activation of T helper 1 (Th1) cells and macrophages that accumulate at the site of inflammation and release cytokines, chemoattractants, and growth factors such as TNF-α, interleukin (IL) 12, interferon γ (INF-γ), IL-18, and transforming growth factor β, among others.1,2 TNF-α is overexpressed in sarcoidosis and is critical to the pathogenesis of granulomas. Proposed mechanisms include proapoptotic activities and pathogenic role in clearing the implicated antigen, both of which can lead to granuloma formation and subsequent fibrogenesis.3