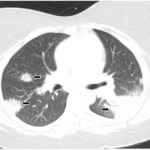
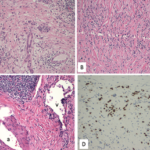
TNF-α inhibitors have been thought to suppress granuloma formation and have been tried in the treatment of refractory sarcoidosis, with varying results.4 Therefore, the development of sarcoidosis in our patients treated with TNF-α inhibitors is an unexpected occurrence. To our knowledge, this is the first case of sarcoidosis development in a psoriatic arthritis patient treated with adalimumab.
There are differences among the different classes of TNF-α inhibitors and the way they can be related to the development of sarcoidosis.5,6 For example, the TNF-α monoclonal antibodies, infliximab and adalimumab, can cause cytotoxic complement-induced lysis of cells expressing membrane-linked TNF-α and cell apoptosis in T cells. In contrast, the soluble TNF-α receptor, etanercept, does not fix complement and does not induce apoptosis.2,4 This may explain etanercept’s more frequent association with the formation of granulomas.2 When TNF-α inhibitors were used in the treatment of sarcoidosis, infliximab was associated with significant improvement, whereas etanercept was associated with worsening disease in patients with progressive pulmonary sarcoidosis.4,7
There has also been a suggestion of an infectious etiology, mainly mycobacterial infection, being associated with the development of sarcoidosis.1 Mycobacterial infections have been reported as an adverse event of treatment with TNF-α inhibitors. It is possible that TNF-α inhibitors may allow or reactivate a mycobacterial infection, which could be linked to sarcoidosis pathophysiology.
In summary, we report two cases of sarcoidosis in patients with psoriatic arthritis following the use of TNF-α inhibitors—one with etanercept, a soluble receptor, and one with adalimumab, a monoclonal antibody. As physicians, we need to be aware of the possibility of sarcoidosis development while treating patients who have psoriatic arthritis with TNF-α inhibitors.
Dr. Cote is a fellow in the department of rheumatology, Dr. Harrington is assistant director of rheumatology, Dr. Meadows is a fellow in the department of internal medicine, Dr. Lin is director of anatomic pathology, and Dr. Bili is a rheumatologist and investigator; all are at Geisinger Medical Center in Danville, Pa.
References
- Hamzeh, N. Sarcoidosis. Med Clin N Am. 2011;95: 1223-1234.
- Massara A, Cavazzini L, Corte, R, et al. Sarcoidosis appearing during anti-tumor necrosis alpha therapy: A new “class effect” paradoxical phenomenon. Two case reports and literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;39:313-319.
- Antoniu S. Targeting the TNF-α pathway in sarcoidosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010;14:21-29.
- Doty J, Mazur J, Judson M. Treatment of sarcoidosis with infliximab. Chest. 2005; 127:1064-1071.
- Wallis R, Ehlers S. Tumor necrosis factor and granuloma biology: Explaining the differential infection risk of etanercept and infliximab. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 34:34-38.
- Mitoma H, Horiuchi T, Tsukamoto H, et al. Mechanisms for cytotoxic effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents on transmembrane tumor necrosis factor α-expressing cells. Comparison among infliximab, etanercept and adalimumab. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:1248-1257.
- Utz JP, Mazur JE, Judson MA. Etanercept for the treatment of stage II and III progressive pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest. 2003;124:177-185.