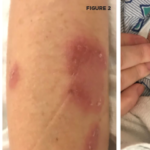
Different kinds of skin lesions are seen in approximately 80% of patients with BS. Acne-like lesions or papulo-pustular lesions are mainly of cosmetic concern because they are frequently seen at both the usual acne sites, such as the face, upper chest, and upper back, and at uncommon sites, such as the legs and arms. Nodular lesions are observed in 50% of the patients and are usually confined to lower limbs in the form of either erythema nodosum–like lesions or superficial thrombophlebitis. It can be difficult to distinguish one lesion from another with the naked eye.
The pathergy reaction is a nonspecific hyper-reactivity of the skin to trauma such as a needle prick (see Figure 2, below). A papule or pustule typically forms 24 to 48 hours after an intradermal injection of the skin with a 20-gauge needle. The pathergy positivity is relatively specific to patients with BS. Although 60% to 70% of patients in Turkey and Japan have a positive pathergy test, it is rarely observed in those with BS from Northern Europe and North America.
Eye disease is seen in half of all patients with BS but is more frequent and more severe in males and young patients. It generally occurs within three to five years of disease onset. The eye disease most commonly seen is a chronic, relapsing, bilateral uveitis involving both anterior and posterior chambers. It is a significant cause of morbidity. Anterior uveitis with intense inflammation (hypopyon) is observed in only a small fraction of patients with eye involvement and is generally associated with severe retinal disease. Isolated anterior uveitis is infrequent and conjunctivitis is rare. Recurrent attacks of eye disease result in structural changes such as synechiae and retinal scars. These events, if left untreated, lead to a loss of vision.
Joint disease is observed in half of the patients with BS in the form of arthritis or arthralgia.2 It is usually mono- or oligoarticular but can be symmetrical. Joint disease resolves in a few weeks and seldom leads to deformity or radiological erosions. The knees are most commonly involved, followed by the ankles, wrists, and elbows. Back pain is relatively rare, and controlled studies have not shown an increased sacroiliac joint involvement.
Patients with BS and arthritis also have more acne lesions. Furthermore, patients with arthritis and acne lesions have significantly higher enthesopathy scores compared with patient without acne,3 suggesting a possible link with acne-associated arthritis.