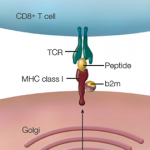
 A growing body of research has revealed a link between Parkinson’s disease and the immune system. Scientists now suspect that inflammation of the microglia plays a role in the degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons affecting Parkinson’s disease. Researchers have also identified a few genetic comorbidities between high-risk Parkinson’s disease loci and immune-related genes. Specifically, they have found a strong pleiotropic enrichment between Parkinson’s disease and Crohn’s disease, suggesting that there may be a common pathogenic link between the two phenotypes.
A growing body of research has revealed a link between Parkinson’s disease and the immune system. Scientists now suspect that inflammation of the microglia plays a role in the degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons affecting Parkinson’s disease. Researchers have also identified a few genetic comorbidities between high-risk Parkinson’s disease loci and immune-related genes. Specifically, they have found a strong pleiotropic enrichment between Parkinson’s disease and Crohn’s disease, suggesting that there may be a common pathogenic link between the two phenotypes.
New research by Aree Witoelar, PhD, postdoctoral researcher at the University of Oslo in Norway, and colleagues provides a novel mechanistic insight into Parkinson’s disease and autoimmune diseases. The research, published online June 5 in JAMA Neurology, identifies a common genetic pathway between the different phenotypes. “We found moderate polygenic pleiotropic enrichment between [Parkinson’s disease] and ulcerative colitis or RA [rheumatoid arthritis], whereas genetic enrichment with Type 1 diabetes, celiac disease, psoriasis and multiple sclerosis was weak,” write the authors.1
The team used a pleiotropy-based statistical framework with coverage greater than 500,000 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Their method considers joint P values and thus, requires SNPs with strong association with Parkinson’s disease to also have a strong association with an autoimmune disease—and vice versa. Because of this approach, the study had a false discovery rate of less than 0.05.
The genome-wide conjunctional analysis identified 17 novel loci with overlap between Parkinson’s disease and autoimmune diseases. These loci included the known Parkinson’s disease loci adjacent to GAK, HLA-DRB5, LRRK2 and MAPT, which were also associated with RA, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. When the scientists replicated the analysis in a different cohort, they were able to confirm the involvement of HLA, LRRK2, MAPT, TRIM10 and SETD1A in Parkinson’s disease. The researchers also identified novel genes that fall within a protein–protein interaction network with known Parkinson’s disease genes. These genes include WNT3, KANSL1, CRHR1, BOLA2 and GLUCY1A3. They note that a subset of these loci are significantly associated with changes in methylation or expression levels of adjacent genes.
“Our brain-based QTL [quantitative trait locus] analyses suggest immune function–related genes for which the expression or methylation level is changed by one of our identified susceptibility loci,” write the authors in their discussion. “Most of these genes are located in the HLA locus or MAPT locus, and owing to the complex underlying LD [linkage disequilibrium] structures, it is difficult to define the true causal genes. However, our analyses implicate that, in addition to the [Parkinson’s disease]-associated HLA genes and MAPT in these loci, TRIM31, CRHR1, PLEKHM1 and NSF might also be related to PD through defective components of the immune system.”