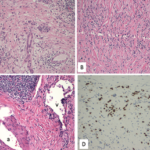
Figure 1: On biopsy, the lung mass lesion showed nodular inflammatory aggregates with residual alveoli and extensive lung fibrosis. Histopathologic image courtesy Dr. Paul Cohen, Yale University.
IgG4-RTIN can be present simultaneously in many cases of IgG4-related membranous glomerulonephritis (IgG4-RMGN) as detected by renal biopsy or suggested by kidney imaging findings (see Table 5). Approximately 7% of TIN cases include concurrent IgG4-RMGN.18 In some cases, glomerular lesions (i.e., IgA vasculitis, IgA nephritis, endocapillary proliferative glomerulonephritis, mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis) have been associated with IgG4-RTIN.19 In membranous nephropathy (MN) associated with IgG4-RD, deposition of IgG4 in the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) has been demonstrated, either predominantly or along with other IgG subclasses. Although idiopathic MN and MN associated with IgG4-RD share a common immunologic process known as Th2 cytokine-mediated immune reaction and subsequent increase of IgG4, those two processes differ in the presence of the anti-PLA2R antibody.20 It has been reported in 70–80% of patients with idiopathic MN, and has been negative in all cases of IgG4-RD and also cases of MN associated with IgG4-RD, suggesting this antibody isn’t involved in the development of IgG4-RD.21
In idiopathic MN, the urine IgG4/IgG ratios were significantly higher in the idiopathic MN group, compared with the minimal-change disease or the focal segmental glomerulosclerosis group.22 Li et al. described a case of IgG4-related MN with high blood and low IgG4/IgG renal clearance ratio. Because IgG4 can engage the Fc of all IgG subclasses with its own Fc, potential binding between IgG4 and other molecules (IgG4 or other subclasses) might occur, and this might increase the molecule size and retard the renal filtration of IgG4. This observation could be a new clue to the different pathogenesis between IgG4-related MN and idiopathic MN, implying that charge selectivity barrier impairment might not occur in the pathogenesis of IgG4-related MN.23
Membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN) may be primary—in that case, it’s called idiopathic—or secondary. The majority of patients with primary MGN have antibodies against the M-type PLA2R antigen.24 MGN secondary to IgG4-RD can be called IgG4-related MGN, although primary MGN is also an IgG4-dominant disease.25 Therefore, immunostaining for IgG subclasses wouldn’t distinguish between primary MGN and IgG4-related MGN. However, staining for PLA2R is positive in the GBMs in the case of primary MGN, with a sensitivity of 74%.26

Table 4: Diagnostic Criteria for IgG4-RKD
Morimoto et al. described a rare case of membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis-like glomerular disease together with tubulointerstitial nephritis in association with AIP, as an organ expression of IgG4-RD.19 Other patterns of renal involvement include glomerular disease, ureteral inflammatory pseudotumor or retroperitoneal fibrosis (RF), which can cause renal failure and chronic sclerosing pyelitis (see Table 5, bottom right).27,28