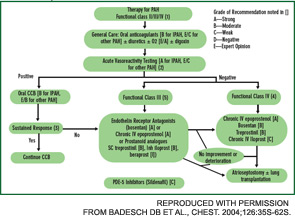
Bosentan, an oral, dual ETA/ETB receptor antagonist has been approved for the treatment of patients with class III or class IV PAH. It improves exercise capacity (6MWT) and hemodynamics, and reduces time to clinical worsening when used in doses of 125 mg bid after an initial month of treatment at 62.5 mg bid. Recent reports suggest that first-line bosentan therapy, with the subsequent addition of other PAH treatments if required, is safe and may prolong survival.12 Bosentan treatment can be associated with untoward effects—hepatotoxicity, anemia, teratogenecity, etc. Monitoring of liver tests is required prior to initiating bosentan therapy and monthly thereafter. Exclude pregnancy and encourage patients to prevent it by two forms of birth control.
Sildenafil is a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor approved for the treatment of patients with class II, III, or IV PAH. In doses of 20, 40, or 80 mg tid, sildenafil improves exercise capacity, hemodynamics, and functional class. More studies are needed before it can be determined if sildenafil improves time to clinical worsening or improves survival. The recommended starting dose is 20 mg tid. Sildenafil is well tolerated but may cause headache, flushing, dyspepsia, and epistaxis. A clinical trial is underway to assess the efficacy and safety of bosentan and sildenafil combination therapy.
PGI2 and its analogues are approved for the treatment of patients with class III or IV PAH. Epoprostenol is administered by continuous intravenous infusion, whereas trepostinil can be administered by subcutaneous or intravenous infusion. Sudden interruption in drug delivery may be complicated by extreme elevation of pulmonary artery pressure. Administer iloprost by inhalation six to nine times daily. Combination therapy with bosentan and inhaled iloprost improves exercise capacity and time to clinical worsening.
Conclusion
Great strides have been made in understanding and managing the major pulmonary complications of SSc, and the prospect of even better treatment has never been greater. Management of SSc lung disease requires the combined skills of the rheumatologist, pulmonologist, radiologist, and cardiologist. The rheumatologist plays a vital role in this process, first by exercising a high index of suspicion to ensure early diagnosis, and then by coordinating the complex management of the SSc patient. Rheumatologists are in the unique position of seeing patients prior to the development of end-stage ILD or PAH. It is our responsibility to see that SSc patients undergo full evaluation for what are now treatable complications of their disease.
