Conclusion: On average and in the absence of TNF inhibitors, patients hospitalized with ankylosing spondylitis do not show an appreciable increased risk of lymphoma.
Commentary
In a time when there is significant discussion in the medical community and press regarding the risk of lymphoma in patients treated with anti-TNF agents, Askling and colleagues’ article is an important and welcome addition to the current state of knowledge.
To date, there has been little published regarding risks of malignancies in patients with AS or other spondyloarthropathies—with the exception of those who received radiation treatment in past decades. Of the two prior publications found on Medline, the first is from the same authors examining a Swedish population-based cohort prior to the use of anti-TNFs. They reported a standardized incidence ratio of 1.34 (CI 0.93–1.89) for all hematopoietic cancers. The second is an abstract that’s not easily available for review.
There are limitations to this study—particularly with the use of an inpatient discharge registry to identify patients with a diagnosis of AS, which may limit generalizability. Conversely, the patients who require hospitalization may represent a sicker population. In light of the recent studies suggesting that chronic inflammation may be a contributing factor to lymphoma origin in RA, studying a sicker population may be appropriate. Additional potential limitations include the lack of disease severity measurements and the overall small numbers despite using an entire country’s registry. However, these limitations should not overshadow the fact that this is a well designed and executed study that highlights the strengths of an organized data collection system.
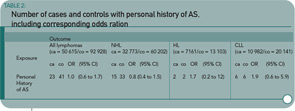
The published data suggest that there is not a significant increase in lymphoma risk—certainly not of the magnitude seen with RA. (See Table 2, below.) The distinct disease pathophysiology may contribute to the differences in lymphoma rates. Or perhaps it may be simply the differences in levels of chronic inflammation, which are generally lower in the AS patient.
In summary, this article draws attention to the need estimate lymphoma risk in patients with AS and other spondyloarthropathies prior to the use of anti-TNF agents from other populations. In future studies addressing this knowledge gap, authors should gather information on measures of disease severity, cumulative disease activity, and disease duration in patients to allow us to explore the potential contribution of inflammation in an epidemiological fashion. Similar questions regarding the potential increased risk of lymphoma in the setting of anti-TNF agents are bound to arise, and without background data, the true answer will never be realized or understood.