Cadherin-11 May Be a Therapeutic Target in RA
By Mary Corr, MD
Lee DM, Kiener HP, Agarwal SK, et al. Cadherin-11 in synovial lining formation and pathology in arthritis. Science. 2007;315(5814):1006-1010.
Abstract
The normal synovium forms a membrane at the edges of joints and provides lubrication and nutrients for cartilage. In RA, the synovium is the site of inflammation, and it participates in an organized tissue response that damages cartilage and bone. We identified cadherin-11 as essential for development of the synovium. Cadherin-11–deficient mice have a hypoplastic synovial lining, display a disorganized synovial reaction to inflammation, and are resistant to inflammatory arthritis. Cadherin-11 therapeutics prevent and reduce arthritis in mouse models. Thus, synovial cadherin-11 determines the behavior of synovial cells in their proinflammatory and destructive tissue response in inflammatory arthritis.
Commentary
RA is a debilitating disease marked by bone and cartilage destruction. In the rheumatoid synovium, the fibroblast cells aggressively proliferate and invade the other joint structures. Indeed, these fibroblast-like synoviocytes develop genetic and phenotypic features similar to malignant cells, including expression of proto-oncogenes and loss of contact growth inhibition. Although these cells in the pannus locally invade, they never metastasize. Most of the current therapies for RA are directed toward other components of the immune system. There has been limited investigation into therapies that are directed against the aggressive behavior of the synovial fibroblasts. By targeting cadherin-11, an essential adhesion molecule for synovial development and mature architecture, Lee and colleagues are paving the way for another approach in our therapeutic armamentarium.
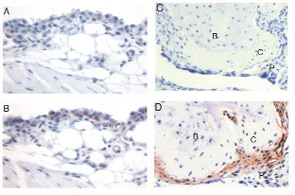
Source: Science. 2007;315(5814):1007.
In a normal diarthrodial joint, the synovial lining is composed of synoviocytes that form an intact layer through cell-to-cell contacts with intervening matrix spaces. Cadherins are a family of adhesion molecules that bind to other cadherin molecules on neighboring cells. Cadherin-11 has a key role in mediating fibroblast-like synoviocyte intercellular adhesion and synovial tissue organization. (See Figure 1) Mice that are genetically deficient in cadherin-11 have a hypoplastic synovial lining. When challenged with arthritogenic antibodies, cadherin-11–deficient mice developed less paw swelling than normal mice and the synovial tissue appeared to lack the usual dense organization on histological examination. In this experiment, fibroblasts in the local microenvironment appeared necessary for the full function of other cell types in the inflammatory process.
