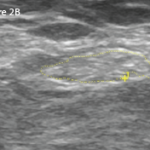
“It was interesting to see that the disease could be initially controlled with relatively little steroid in the control group,” adds Dr. Goronzy, “but this may come at the price of more smoldering disease in the second year,” an observation that he says should be confirmed in a larger study.

Exercise Prior to Arthroplasty Increases Chances of Home Discharge
A patient’s chance of being discharged directly home after major joint arthroplasty increases significantly when the patient engages in a presurgical exercise program, according to a study published in Arthritis Care & Research (2006;55(5):700-709).
The magnitude of the exercise effect was “startling,” lead author Daniel S. Rooks, ScD, assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston, tells The Rheumatologist.
The potential role of exercise in preparation for joint replacement surgery has received little attention, Dr. Rooks and his coauthors write. They studied the impact of a six-week preoperative exercise program on postoperative function, pain, and muscle strength among people undergoing primary, unilateral total knee or hip arthroplasty.
The authors enrolled 63 patients scheduled for total hip arthroplasty and 45 for total knee arthroplasty. Patients randomized to the exercise program performed cardiovascular, strength, and flexibility exercises three times a week for the six weeks prior to surgery. Patients in the control group received educational handouts in the mail and weekly follow-up phone calls. All participants were evaluated on pain, functional status, and muscle strength at baseline, after the six-week intervention period, and at eight and 26 weeks after surgery.
Sixty-five percent of the patients who exercised were discharged directly to home following surgery, compared with 44% in the control group. The remaining patients were discharged to a rehabilitation facility. All in all, exercisers were 73% more likely to be discharged to home, compared with the controls. “I think that participating in the exercise program helped people physically and mentally prepare for in-hospital rehabilitation immediately following surgery, which enabled them to be better prepared to manage their health at home,” says Dr. Rooks.
Physical function improved significantly among patients scheduled for total hip arthroplasty by the end of the six-week exercise period, while it worsened in the control patients. Total knee arthroplasty exercisers demonstrated a 20% increase in leg-press strength compared with the controls, but this did not translate into a corresponding improvement in function or decrease in pain, suggesting that the outcomes depended to some extent on joint location, the authors write.