BALTIMORE—There’s an increasing interdisciplinary interest in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease, according to Colorado-based rheumatologist Aryeh Fischer, MD, the lead author of a special article about an international summit of experts on the topic. The article was co-published in the February 2019 issues of the ACR’s journal Arthritis & Rheumatology, as well as the Association of Physicians of Great Britain and Ireland’s QJM: An International Journal of Medicine.1
“There’s a growing appreciation for unmet needs, challenges and opportunities in this domain,” Dr. Fischer says.
The summit, held Nov. 15, 2018, at a meeting of the Maryland Society for the Rheumatic Diseases, fostered dialogue on key clinical and research aspects of the complex intersection between connective tissue diseases (CTDs)—a group of heterogeneous systemic autoimmune disorders—and interstitial lung disease (ILD). During the one-day summit, physicians and researchers proposed initiatives to raise awareness of the intersection between these diseases, research initiatives and clinical trial possibilities with novel therapeutic agents to better serve patients with autoimmune forms of ILD and improve the quality of their lives.
The summit’s proceedings were organized around five areas:
- Clinical;
- Biomarkers;
- Diagnostic imaging and histopathology;
- Treatment and clinical trials design and outcome measures; and
- Translational research.
The Complexities of ILD
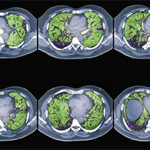
ILD, an overarching term for a group of lung disorders characterized by scarring and/or inflammation in the lung parenchyma, is a common manifestation of CTD and often results in significant morbidity and mortality. Although all CTD patients can develop ILD, those with systemic sclerosis, polymyositis/dermatomyositis and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at particularly high risk.
A patient with CTD can develop ILD at any time, but ILD may also present as the first clinically apparent feature of an otherwise undiagnosed CTD. Diagnosing CTD-associated ILD as early as possible can help determine treatment decisions, assist with surveillance for other autoimmune clinical features, as well as help ascertain a patient’s prognosis. And although ILD can be devastating and progressive, as in the case of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, some CTD patients develop mild forms of ILD that are not progressive in nature.
Collaboration
The summit underscored that collaboration among rheumatologists and pulmonologists is key to accurately diagnosing, evaluating and treating patients with these diseases.

Attendees of the summit discussed key clinical and research aspects of the complex intersection between connective tissue diseases and ILD.
“There is a growing appreciation that this is not a rheumatology problem or a pulmonology problem in isolation,” says Dr. Fischer. “Essentially, this [care] is reaching across the aisle with respect to interdisciplinary engagement. Pulmonologists need to engage rheumatologists. Rheumatologists need to engage pulmonologists, and we need to work together to provide better education.”