The prophylactic use of pentoxifylline & tocopherol two to three weeks prior to a dental extraction & continued therapy post extraction until the surgical site completely heals have been shown to reduce the incidence of MRONJ.
Autologous Platelet Concentrates
In 1998, Marx et al. reported the use of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) as an accelerator in bone healing by influencing bone regeneration. PRF is obtained by sequestering and concentrating platelets by gradient density centrifugation.15 It is an autogenous source of platelet-derived growth factors, transforming growth factor β1 and transforming growth factor β2.15 Hence, PRF is responsible for enhancing the rate of wound healing and new bone formation. Since 1998, autologous platelet concentrates have gained popularity in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Its advantages and beneficial effects for improved soft tissue and bone healing have been validated in several other oral surgery procedures, as well.
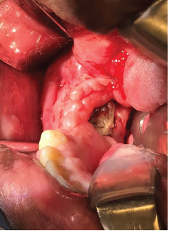
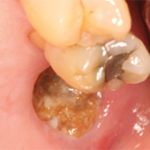
Exposed bone in the right mandible.
In 2007, Adornato et al. reported their experience using platelet-derived growth factors in managing refractory cases of MRONJ in 12 patients. They treated patients with a combination of the removal of necrotic bone and the application of PRF with resorbable collagen membrane.16 This therapy showed positive results, including complete wound healing, reduced treatment periods, less pain and improved quality of life.16
In 2012, Bocanegra-Perez et al. carried out a prospective descriptive study that included eight patients with a diagnosis of MRONJ. These patients were treated surgically with debridement of necrotic bone, followed by the application of leukocytes and PRF, and primary closure of the surgical site. The patients remained asymptomatic without dehiscence and evidence of exposed bone after an average 14-month follow-up period.17
PRF appears to be an accelerator of wound healing, preventing the occurrence of MRONJ in patients on bisphosphonate therapy undergoing tooth extraction.
In 2012, Mozzati et al. performed a case-control study on 176 patients requiring tooth extraction who were treated with intravenous zoledronic acid therapy. They divided the cohort into two groups: study and control groups. The study group, comprising 91 patients, was treated with plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) post-extraction. The control group of 85 patients was not treated with PRGF post-extraction. They concluded that PRGF placement post-extraction reduces the risk of osteonecrosis of jaws.18
In 2017, Asaka et al. published their study, conducted at Hokkaido University Graduate School of Dental Medicine, Sapporo, Japan, of patients requiring tooth extraction who received oral bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis. A total of 102 patients met the inclusion criteria, which consisted of patients requiring tooth extraction who were on oral bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis or glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis for more than one year.
The study compared a prospective cohort of patients treated with platelet-rich fibrin against historical controls.19 The PRF group consisted of 29 patients; the control group was made up of 73 patients.19 These patients had received oral bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis for an average of 32 months.19 Early epithelialization was confirmed in all PRF patients, and the prevalence of delayed recovery was significantly higher in the control group than in the PRF group.19 Thus, use of PRF may reduce the risk of delayed recovery in patients undergoing oral bisphosphonate therapy.