Dr. Fernandez suggested that rheumatologists use validated objective scoring tools for cutaneous involvement, such as the Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Activity and Morphology Instrument (CSAMI) and Sarcoidosis Activity and Severity Index (SASI). According to Dr. Fernandez, these tools can be useful in real-world clinical settings to follow progression or improvement of cutaneous disease by various specialists who treat sarcoidosis patients.
“Although local therapies are excellent when patients have mild disease,” said Dr. Fernandez, “Hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate and TNF inhibitors are effective for patients requiring systemic treatment.” He also pointed out that JAK inhibitors are emerging as a treatment option and described a recent case series of five patients with refractory cutaneous sarcoidosis who were successfully treated with the JAK inhibitor, tofacitinib.5
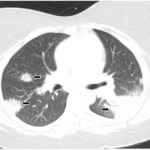
The patients in the case series had a mean treatment duration of 6.4 months and all five patients achieved CSAMI minimal clinically important differences with tofacitinib, and two achieved complete response at eight months. Additionally, three patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis reported cough reduction and improved exercise tolerance. Lastly, serial high-resolution computed tomography imaging in one patient showed progressive resolution of radiologic changes.
Lara C. Pullen, PhD, is a medical writer based in the Chicago area.
References
- MJ Bradshaw, Pawate S, Koth LL, et al. Neurosarcoidosis pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021 Oct 4;8(6):e1084.
- Stern BJ, Royal W III, Gelfand JM, et al. Definition and consensus diagnostic criteria for neurosarcoidosis: From the Neurosarcoidosis Consortium Consensus Group. JAMA Neurol. 2018 Dec 1;75(12):1546–1553.
- Schupp JC, Freitag-Wolf S, Bargagli E, et al. Phenotypes of organ involvement in sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2018 Jan 25;51(1):1700991.
- Trilleras-Gomez AP, Hull KJ, Drew DZ. Case report and review of 7 similar cases in the literature: Cutaneous sarcoidosis as side effect of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in stage IV squamous cell carcinoma of lung. J Immunother. 2021 Feb–Mar 1;44(2):90–94.
- Kerkemeyer KL, Meah N, Sinclair RD. Tofacitinib for cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoidosis: A case series. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021 Feb;84(2):581–583.