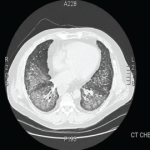
The PL-7 antisynthetase syndrome is the third most common of the antisynthetase syndromes (after Jo-1 and PL-12).5 Most patients have myositis. Interstitial lung disease is the second most common manifestation. To date there are only case reports and small case series on the use of rituximab in the antisynthetase syndrome. Sem et al reported on 11 patients with antisynthetase syndrome who had previously failed treatment with cyclophosphamide or other immunosuppressive treatment.6 The interstitial lung disease stabilized or improved in seven of 11 patients with the antisynthetase syndrome at six months follow-up. There was one fatal infection three months after rituximab. Otherwise, the drug was well tolerated in these patients.
No retrospective or prospective studies have yet evaluated rituximab as a first-line agent for this indication. In our patient with PL-7 antisynthetase syndrome, at three months follow-up, rituximab has proven to be successful as a first-line steroid-sparing agent.
Dr. Rastalsky is a fellow in rheumatology at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
Send us Your Case Suggestion
Have you managed a patient with an unusual rheumatologic problem that you would want to present to a larger audience? Consider submitting your case to The Rheumatologist.
We are looking for interesting cases that are well written and provide useful teaching points to the reader. Send an outline of your case presentation to Simon Helfgott, MD, at [email protected], or visit www.The-Rheumatologist.org for more information.
References
- Dickey BF, Myers AR. Pulmonary disease in polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1984; 14:60.
- Betteridge Z, Gunawardena H, North J, et al. Anti-synthetase syndrome: A new autoantibody to phenylalanyl transfer RNA synthetase (anti-Zo) associated with polymyositis and interstitial pneumonia. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007; 46:1005.
- Schulte-Pelkum J, Fritzler M, Mahler M. Latest update on the Ro/SS-A autoantibody system. Autoimmun Rev. 2009; 8:632.
- Bloch D. The anti-Ro/SSA and anti-La/SSB antigen-antibody systems. Uptodate.
- Labirua-Iturburu A, Selva-O’Callaghan A, Vincze M, et al. Anti-PL-7 (anti-threonyl-tRNA synthetase) antisynthetase syndrome: Clinical manifestations in a series of patients from a European multicenter study (EUMYONET) and review of the literature. Medicine. 2012; 91 (4): 206-211.
- Sem M, Molberg O, Lund MB, Gran JT. Rituximab treatment of the anti-synthetase syndrome—A retrospective case series. Rheumatology. 2009; 48: 968–971.