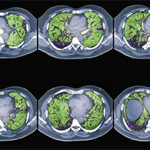
Van Selby, MD, assistant professor of medicine in cardiology at UCSF who works frequently with rheumatologists for patients who have PH, offered additional perspectives on PH and PAH during the lung disease panel at CRA. “Sometimes we use these two terms interchangeably, but it’s important to know which is which. Get familiar with the WHO classification of PH,” he urged attendees. Patients with PH should be referred to someone who has experience treating the condition, whether pulmonologist or cardiologist, Dr. Selby said. Some cardiologists may not be comfortable with it, “but we work closely with rheumatologists all the time for co-management of PAH in systemic sclerosis and other kinds of connective tissue diseases.”
Supportive therapy is also critical for these patients, including exercise. “Have patients start out easy and watch closely for chest pain, dizziness or fatigue. Cardiac or pulmonary rehabilitation programs where they are closely monitored are also helpful.” Other supportive measures include diuretics, digoxin, supplemental oxygen, oral anticoagulants and iron supplementation.
In terms of treatment for CTD-related PAH, an upfront two-drug strategy demonstrated superiority in the huge AMBITION trial comparing initial combination versus monotherapy with tadalafil and ambrisentan, Dr. Selby said.6 “That was a game changer for me and for the pulmonary hypertension community. People are now even studying initial therapy with more than two drugs. The idea is to hit it hard, as early as possible.” This includes treatment of PAH associated with systemic sclerosis, which can be hard to treat. “The last decade has seen many new medications approved for the treatment of PAH. The guidelines are still trying to find the optimal initial approach for each patient.”
Ultimately, once lung function drops below a certain level, lung transplant may be the only long-term treatment option for some of these patients. The speakers encouraged early referral to a transplant center to get patients assessed and enrolled on the transplant list before their condition is too far advanced.
Larry Beresford is an Oakland, Calif.-based freelance medical journalist.
References
- Tashkin DP, Roth MD, Clements PJ, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil versus oral cyclophosphamide in scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SLS II): A randomised controlled, double-blind, parallel group trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2016 Jul 25. pii: S2213–S2600(16)30152–30157. Epub ahead of print.
- King TE, Brandford WZ, Castro-Bernardini S, et al. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014 May 29;370(22):2083–2092.
- Richeldi L, duBois RM, Raghu G, et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014 May 29;370(22):2071–2082.
- Simonneau G, Robbins I, Beghetti M, et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009 Jun 30;54(1 Suppl):S43–S54.
- Badesch DB, Raskob GE, Elliott CG, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: Baseline characteristics from the REVEAL Registry. Chest. 2010 Feb;137(2):376–387.
- Galie N, Barbera JA, Adaani EF, et al. Initial use of ambrisentan plus tadalafil in pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2015 Aug 27;373(9):834–844.