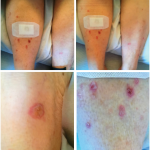
All 15 cases reported by Calabrese et al. required glucocorticoids, and three required a biological agent. Of those, 10 patients required their immunotherapy to be either permanently or temporarily discontinued.3 Given our patient’s advanced cancer, TNF inhibitors were not initiated. Methotrexate could have been an option for our patient, but he had a history of hepatitis C, and there are limited data on irAEs with methotrexate use.6 One of the patients reported by Calabrese et al. experienced a flare of psoriatic arthritis and was treated with apremilast with good response while remaining on immunotherapy.3 Apremilast was discussed as a potential therapy option with our patient, but unfortunately, he failed to follow up in the rheumatology clinic.
Conclusion
This case highlights an important emerging complication related to cancer immunotherapy with nivolumab, and it highlights the need for physicians to maintain a low threshold to suspect irAEs in patients on immunotherapy to achieve a timely diagnosis and initiate appropriate treatment.
Catherine Strahle, DO, is an internal medicine resident at the Department of Internal Medicine at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine.
Nathalie E. Chalhoub, MD, is a rheumatology fellow at the Division of Immunology, Allergy and Rheumatology and an outcomes research fellow in the Internal Medicine Scholars Training for Academic Research (IMSTAR) program at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine.
Avis Ware, MD, is a professor of medicine at the Division of Immunology, Allergy and Rheumatology at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, and the Rheumatology Clinical Director at University of Cincinnati Health.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Christine L. Chhakchhuak, MD, for being part of the patient’s care and for all her efforts in coordinating the treatment plan with the patient’s oncologist.
References
- Abdin SM, Zaher DM, Arafa EA, et al. Tackling cancer resistance by immunotherapy: Updated clinical impact and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 2018 Jan 25;10(2). pii: E32.
- Kommalapati A, Sikder S, Tella S. Immune check point inhibitors in cancer therapy: Beware of “friendly fire” effect. Res Rev J Hosp Clin Pharm. 2017 Jul; 3(2):5–6.
- Calabrese C, Kirchner E, Kontzias A, et al. Rheumatic immune-related adverse events of checkpoint therapy for cancer: Case series of a new nosological entity. RMD Open. 2017 Mar 20;3(1):e000412.
- Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015 Jul 2;373(1):23–34.
- Cappelli LC, Shah AA, Bingham CO. Immune-related adverse effects of cancer immunotherapy—implications for rheumatology. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2017 Feb;43(1):65–78.
- Cappelli LC, Gutierrez AK, Baer AN, et al. Inflammatory arthritis and sicca syndrome induced by nivolumab and ipilimumab. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jan;76(1):43–50.