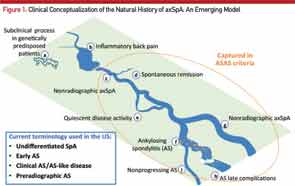
Here, the course of axial SpA is compared to the course of a river. A) Some people may be genetically predisposed to develop axial SpA but may never develop any clinical manifestations of the condition or may have a subclinical disease. B) According to the recent NHANES study (2009–2010), inflammatory back pain is found in 6% of U.S. population, but only a small percentage of those will develop C) nonradiographic axial SpA (nr-axSpA). D) A small percentage of these people may have a spontaneous remission, and E) some may have a quiescent disease course. F) Studies have shown that up to 12% of nr-axSpA patients develop ankylosing spondyloarthritis (radiographic sacroiliitis) in two years; whereas, others may continue as G) nr-axSpA. Not all ankylosing spondylitis patients have a progressive course, either. Some progress to develop long-term complications H), and others may have a relatively benign but chronic course I). Adapted from van Vollenhoven RF. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011 Apr;7(4):205–215.
MRI of the sacroiliac (SI) joints has emerged as the imaging investigation of choice for patients with suspected axSpA who do not have X-ray evidence of sacroiliitis. On T2-weighted fat-suppressed sequences (called STIR sequences) of the MRI, active inflammatory lesions of osteitis are seen as bone marrow edema (BME). MRI can also detect other lesions, such as synovitis, enthesitis and capsulitis, associated with SpA. Among these, the clear presence of a single osteitis lesion on two consecutive slices or two osteitis lesions on a single MRI slice is considered essential for defining active sacroiliitis.8 Structural damage lesions, such as sclerosis, erosions, fat deposition and ankylosis can also be detected by MRI on T1-weighted images.9
Although an MRI scan of the SI joints is progressively used in the early diagnosis of nr-axSpA, it has several limitations. The BME seen on STIR images used to diagnose sacroiliitis can also be seen in normal adults, young patients with trauma and older patients with degenerative arthritis of the SI joints. Also, because AS patients have intermittent sacroiliac joint inflammation, the absence of BME cannot rule out axSpA. Signs of structural damage on T1-weighted images of the SI joints described above could increase the specificity of the diagnosis,9 although the exact location for structural damage lesions for diagnosis and classification is less clear.
Finally, as with every other diagnosis in rheumatology, expensive investigations can only supplement and not replace the thoughtfulness that goes into making an accurate clinical diagnosis. Ordering HLA-B27 or an MRI scan of the SI joints in patients who have no other features of SpA or whose back pain started after the age of 45 should be avoided.
Prevalence
Axial spondyloarthritis may be as prevalent as rheumatoid arthritis, and nr-axSpA has disease burden comparable to AS.