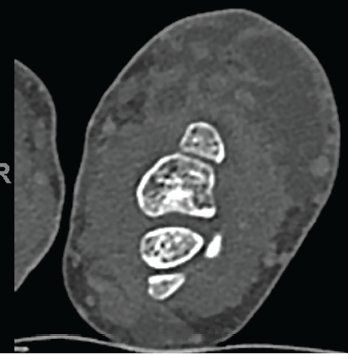
Figure 3. Multiloculated fluid collections in the dorsal subcutaneous tissue of the distal ulna seen on CT scan.
Given her escalating back pain and the finding of this organism, repeat CT imaging of the spine was performed to search for other infection sites. This showed degenerative changes of the thoracic spine and postsurgical changes of the lower lumbar spine, with interval improvement of the paraspinal soft tissues but no evidence of infection.
A drug sensitivity panel showed resistance to ciprofloxacin, but sensitivity to moxifloxacin, clarithromycin, amikacin, streptomycin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, linezolid, ethambutol, isoniazid, rifampin and rifabutin.
In December 2018, following slow but progressive postoperative wound healing, she developed increased purulent drainage (see Figure 5, p. 61), concerning for paradoxic worsening vs. treatment failure vs. bacterial superinfection. Antimycobacterials were temporarily held, and she underwent repeat debridement, specimens from which again showed M. kansasii, with broth-only culture showing coagulase-negative Staphylococcus.
Antimycobacterial therapy was subsequently reinitiated. She developed a whole body maculopapular rash attributed to rifabutin, so 5 mg/kg of intravenous amikacin three times per week was substituted, and the rash resolved. She completed a 15-week course of amikacin and was continued on azithromycin and ethambutol.
She developed nodular lesions on the left palm, two digits, as well as the right ventral wrist, in December 2018. White caseating material was expressible from these, and moxifloxacin was added to intensify the regimen in case these represented M. kansasii satellite lesions; she developed a prolonged QTc, so this was soon stopped.
She was continued on her two-drug regimen of azithromycin and ethambutol.
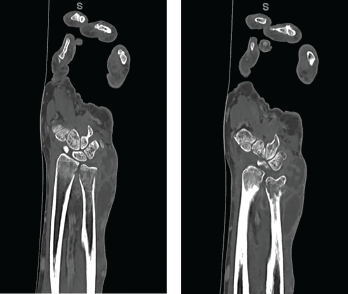
Figures 4a and 4b CT scan showing (a) a radial focus of bone destruction in the ulnar aspect of the distal left radius and (b) ulnar periostitis and bone destruction of the distal left ulna.
Plain films in late December 2018 showed progressive disease, so she underwent repeat operative debridement in early February 2019. Surgical cultures grew coagulase-negative Staphylococcus in three cultures (sensitive only to gentamycin, tetracycline and vancomycin), but did not grow M. kansasii. She was not started on additional antimicrobials because she had no symptoms of cellulitis or increased drainage from the wound. She had poor, postoperative wound healing, so she completed 45 sessions (five sessions per week) of hyperbaric oxygen therapy between March 2019 and May 2019.
The patient was seen urgently in late May 2019 for purulent drainage and wrist swelling, and underwent another operative debridement. Cultures showed Peptostreptococcus (tissue) and rare Corynebacterium (bone). She received vancomycin preoperatively and was discharged on doxycycline to complete a 14-day course. Subsequently, 200 mg of tedizolid daily was added to her regimen for both M. kansasii and Corynebacterium coverage.
Drainage from her wrist stopped in June 2019 (see Figure 6, opposite). At follow-up in November 2019, her left wrist wound was completely healed, without any further discharge. Her antimycobacterials were stopped, given a total of one year of treatment.