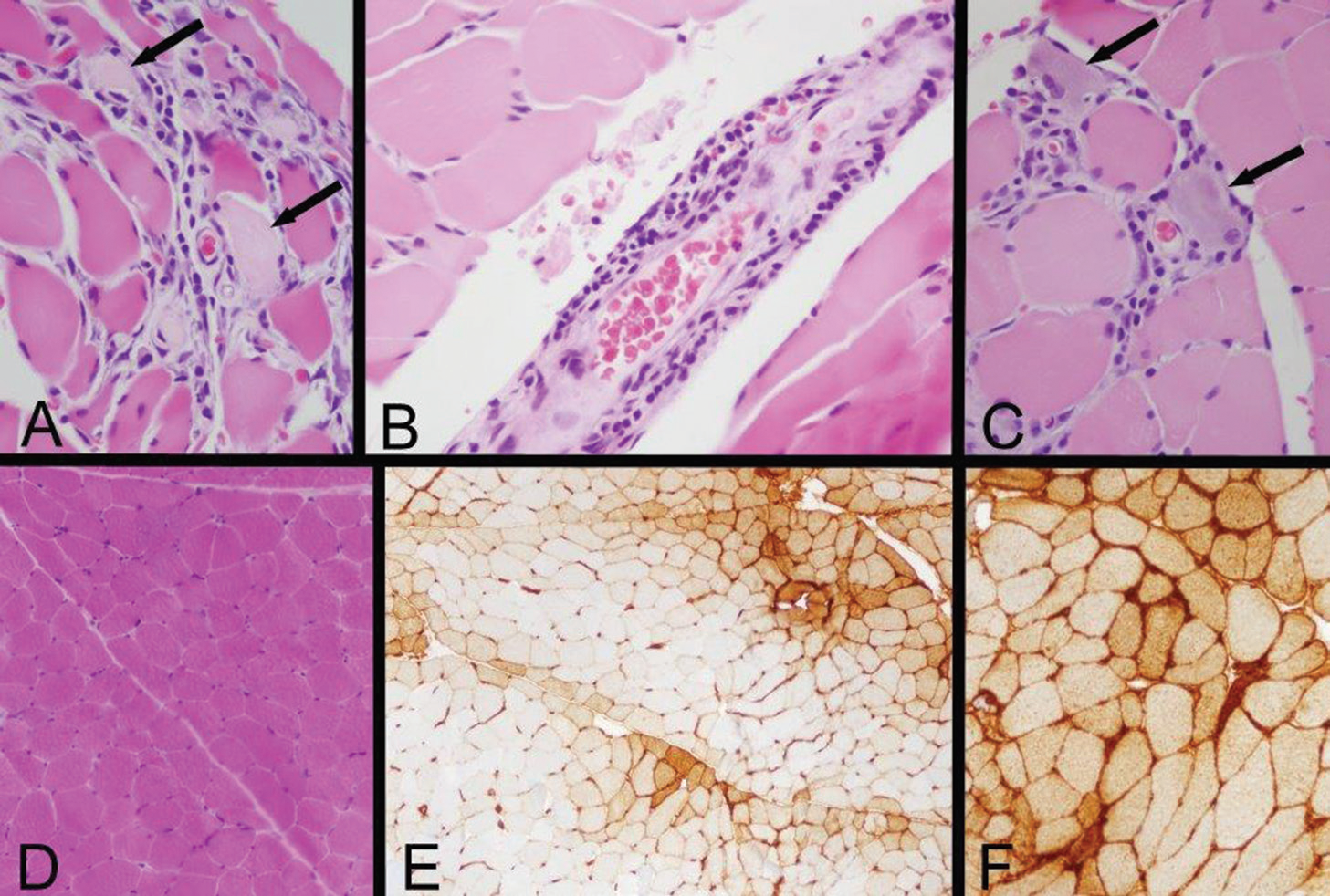
Figure 2: Left Quadriceps Muscle Biopsy
A: Two necrotic myofibers with pale sarcoplasm are identified by arrows in this area of a paraffin hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) section, which also exhibits very mild endomysial lymphocytic inflammation.
B: A mild perimysial perivascular lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate is present in this region of a paraffin H&E section.
C: Arrows indicate two regenerating myofibers, which are identified by their basophilic cytoplasm and large nuclei with nucleoli, and a small number of lymphocytes infiltrate this zone (paraffin H&E). Inflammation associated with necrotic or regenerating myofibers may be a reactive change rather than evidence of an inflammatory myopathy; the perivascular inflammation provides more convincing evidence of an immune-mediated myopathy.
D: A low-power view of a portion of a cryostat H&E section illustrates that much of the biopsy has no inflammation and no myofiber necrosis or regeneration.
E: Human leucocyte antigen Class ABC or Class I (HLA Class I) immunohistochemistry exhibits labeling of many myofibers, indicated by the brown staining. In this area, there is a somewhat perifascicular concentration of positive myofibers.
F: HLA Class I immunohistochemistry shows strong surface labeling and sarcoplasmic staining of all of the myofibers in this area. Original magnifications: A, B, C—400x; D, E—100x; F—200x
The constellation of findings, temporal association of events and presence of multi-organ involvement raised suspicion for an immunotherapy-mediated toxicity. The patient was started on 1 mg/kg of methylprednisolone immediately after the muscle biopsy. The choice of steroid dosing was based on guidelines for management of the known toxicities of nivolumab (skin, pneumonitis, neurologic) because no guidelines on the management of myositis or cardiotoxicity secondary to nivolumab therapy were known to have been published at the time.
Within two days of starting steroids, the patient demonstrated improvement in her respiratory status and stridor. On Day 3, she was able to sit up without assistance. By Day 7, her dysphagia and dysphonia were significantly improved, and the nasogastric tube was removed. Her dyspnea also improved, and the patient no longer required oxygen for relief. An ultrasound of the diaphragm following the steroid treatment showed appropriate movement with respiration. Her ptosis resolved, and the rash gradually diminished in intensity and size.
By the time of discharge three weeks later, the patient was again able to walk, albeit a few steps. Her lab values had normalized: CK of 126 IU/L, troponin of 0.3 ng/mL, ALT of 95 u/L and AST of 32 u/L. She was discharged to rehab with an oral prednisone taper.